AI Photo Denoiser: Advanced Noise Removal Technology for Professional Photography
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Digital Noise and Grain
2. The Science Behind AI Denoising
3. Types of Image Noise
4. AI vs Traditional Denoising Methods
5. Professional Photography Applications
6. Technical Implementation
7. Best Practices and Workflows
8. Future of AI Denoising
Digital noise and grain represent one of photography's most persistent challenges, affecting image quality across all genres of photography. From wedding photographers working in dimly lit venues to wildlife photographers capturing subjects in challenging lighting conditions, unwanted noise can compromise the technical and aesthetic quality of images. AI-powered denoising technology has revolutionized how photographers approach noise reduction, offering unprecedented capability to remove unwanted artifacts while preserving critical image details that traditional methods often sacrifice.
The emergence of artificial intelligence in image processing has fundamentally changed the denoising landscape. Where conventional algorithms rely on mathematical interpolation and statistical analysis, AI denoising systems learn from millions of image examples to understand the complex relationship between noise patterns and legitimate image content. This learning-based approach enables more intelligent decision-making about what constitutes noise versus essential image information.
Understanding Digital Noise and Grain {understanding-digital-noise-and-grain}
The Physics of Digital Noise
Digital noise originates from multiple sources within the imaging chain, each contributing different characteristics to the final image degradation. Thermal noise occurs when electrons move randomly within the camera sensor due to heat, creating bright pixels that don't correspond to actual light exposure. This type of noise increases significantly with higher sensor temperatures, which is why long exposures and high-performance cameras often include active cooling systems.
Shot noise represents a fundamental physical limitation based on the quantum nature of light itself. When photons strike the sensor, they arrive randomly rather than in a steady stream, creating statistical variations in the signal. This randomness becomes more apparent in low-light conditions where fewer photons are available to create a stable signal, resulting in visible noise patterns.
Read noise occurs during the electronic conversion of photon-generated charges into digital values. This process inherently introduces small electrical variations that manifest as noise, particularly visible in shadow areas where the actual signal is weak. Modern sensor designs continuously work to minimize read noise through improved electronics and processing techniques.
ISO Performance and Noise Characteristics
Modern Sensor Technology: Contemporary camera sensors demonstrate remarkable improvements in high-ISO performance compared to previous generations. Full-frame sensors generally exhibit superior noise characteristics due to larger individual photosite areas that can capture more light. However, even the most advanced sensors show increased noise at elevated ISO settings.
Sensor Size Impact: The relationship between sensor size and noise performance is fundamental to understanding when denoising becomes necessary. Larger sensors can maintain better signal-to-noise ratios because individual photosites have more surface area to collect light. This is why full-frame cameras typically outperform crop sensors in low-light conditions.
ISO Invariance: Some modern cameras exhibit ISO invariance, meaning similar noise levels can be achieved by underexposing at lower ISO settings and brightening in post-processing versus shooting at higher ISO values. Understanding your camera's ISO performance helps optimize the balance between in-camera settings and post-processing denoising.
Film Grain vs Digital Noise
Aesthetic Differences: Film grain possesses organic, random characteristics that many photographers find aesthetically pleasing. Unlike digital noise, which tends to create regular patterns and color speckles, film grain maintains a more natural, textured appearance. However, when digitizing film photographs, this grain can sometimes interfere with modern viewing and printing requirements.
Preservation Considerations: When working with scanned film photographs, photographers must decide whether to preserve the original grain character or remove it for cleaner presentation. RestoreAI's Denoiser includes specific algorithms trained to distinguish between desirable film grain and unwanted digital artifacts, allowing selective treatment of different noise types.
The Science Behind AI Denoising {the-science-behind-ai-denoising}
Deep Learning Architecture
Convolutional Neural Networks: Modern AI denoising relies primarily on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) that excel at recognizing spatial patterns in image data. These networks learn to identify noise patterns by analyzing millions of image pairs showing the same content with and without noise. The learning process enables the AI to understand complex relationships between noise characteristics and legitimate image features.
Attention Mechanisms: Advanced denoising networks incorporate attention mechanisms that help the AI focus on specific image regions requiring different treatment. These mechanisms allow the system to apply stronger noise reduction in smooth areas like skies while preserving fine details in textured regions like fabric or foliage.
Multi-Scale Processing: Professional AI denoising systems analyze images at multiple resolution scales simultaneously. This approach enables detection of both fine-grained noise patterns and larger structural features that should be preserved during the denoising process.
Training Methodologies
Synthetic Noise Generation: AI denoising networks are trained using millions of high-quality images to which various types of synthetic noise are added. This approach allows the system to learn noise characteristics without requiring paired clean/noisy versions of real photographs. The synthetic noise must accurately represent real-world noise patterns to ensure effective performance.
Real-World Data Integration: The most effective AI denoising systems supplement synthetic training data with real-world noisy images captured under various conditions. This combined approach helps the AI generalize better to actual photography scenarios rather than only laboratory-generated noise patterns.
Transfer Learning: Modern AI denoising development leverages transfer learning, where networks initially trained on general image recognition tasks are fine-tuned specifically for noise removal. This approach accelerates training and often produces superior results compared to training from scratch.
Edge Preservation Technology
Gradient Analysis: AI denoising systems must distinguish between noise and legitimate edges in images. Advanced algorithms analyze local gradients to identify areas where intensity changes represent actual image content versus random noise variations. This analysis enables selective processing that preserves important edges while removing unwanted artifacts.
Texture Recognition: Sophisticated AI denoising recognizes different texture types and applies appropriate processing to each. Smooth gradients receive aggressive noise reduction, while textured areas like fabric, bark, or grass maintain their characteristic patterns without being smoothed away.
Adaptive Processing: The most advanced systems adapt their processing strategy based on local image content. Areas containing faces might receive different treatment than landscapes, and technical subjects like electronics or machinery might be processed differently than organic subjects.
Types of Image Noise {types-of-image-noise}
Luminance Noise
Characteristics and Detection: Luminance noise appears as random brightness variations across the image, creating a speckled or grainy appearance particularly visible in uniform areas like skies or walls. This type of noise is most apparent in shadow areas where the signal-to-noise ratio is lowest. AI algorithms detect luminance noise by analyzing statistical variations in pixel brightness values across similar image regions.
Impact on Image Quality: Luminance noise primarily affects the perceived sharpness and smoothness of images. While generally less objectionable than color noise, excessive luminance noise can make images appear gritty and unprofessional. In commercial photography, even moderate luminance noise can be problematic for large-format printing or detailed inspection.
Processing Strategies: AI denoising systems use sophisticated edge detection to apply luminance noise reduction selectively. Smooth areas receive aggressive processing while textured regions maintain their detail structure. The challenge lies in distinguishing between noise and legitimate fine detail, particularly in subjects like fabric textures or natural surfaces.
Color Noise (Chroma Noise)
Visual Characteristics: Color noise manifests as random color speckles or shifts that don't correspond to actual subject colors. This type of noise is particularly problematic because it creates unrealistic color variations that immediately appear unnatural to viewers. Color noise often exhibits characteristic patterns specific to individual camera models and sensor designs.
Technical Causes: Color noise typically results from imperfections in the color filter array or differences in sensitivity between color channels. High ISO settings amplify these variations, creating visible color artifacts. Digital processing algorithms within cameras sometimes contribute additional color noise during the conversion from RAW sensor data to processed images.
AI Solutions: Advanced AI denoising systems analyze color relationships across the image to identify and correct inappropriate color variations. These algorithms learn normal color patterns for different subject types, enabling intelligent correction of color noise while preserving legitimate color variations and gradients.
Pattern Noise and Fixed-Pattern Artifacts
Source and Characteristics: Pattern noise appears as regular or semi-regular patterns across the image, often resulting from electrical interference or sensor manufacturing variations. Unlike random noise, pattern noise exhibits consistent characteristics that can sometimes be more distracting than purely random artifacts.
Hot Pixels and Dead Pixels: Long exposures can reveal hot pixels that consistently produce bright spots, while dead pixels fail to respond to light at all. AI denoising systems can learn to identify and correct these fixed-pattern artifacts by analyzing pixel behavior across multiple images or using statistical analysis of surrounding pixels.
Banding and Striping: Some cameras exhibit banding patterns, particularly in shadow areas or during high-ISO shooting. These patterns result from variations in sensor readout electronics and can be particularly challenging to correct without affecting legitimate image content. AI systems trained specifically on these patterns can often provide effective correction.
Compression Artifacts
JPEG Compression Effects: While not technically noise, JPEG compression creates artifacts that share similar characteristics with noise and often require similar correction approaches. These artifacts include blocking patterns, ringing around edges, and color bleeding between adjacent areas.
AI Enhancement Integration: Modern AI denoising tools often include specialized algorithms for correcting compression artifacts alongside traditional noise reduction. This integrated approach is particularly valuable when working with images that have undergone multiple compression cycles or aggressive compression settings.
AI vs Traditional Denoising Methods {ai-vs-traditional-denoising-methods}
Limitations of Traditional Approaches
Statistical Filtering: Traditional denoising relies heavily on statistical analysis of pixel neighborhoods, applying mathematical filters that assume noise characteristics follow predictable patterns. While effective for simple noise types, these methods often struggle with complex real-world noise that varies across the image or exhibits non-standard characteristics.
Edge Preservation Challenges: Conventional algorithms face fundamental difficulties in distinguishing between noise and legitimate image details. Aggressive noise reduction often results in over-smoothing that eliminates fine textures and reduces apparent sharpness. Conservative settings may leave visible noise artifacts that compromise image quality.
One-Size-Fits-All Processing: Traditional methods typically apply uniform processing across the entire image, failing to account for varying noise characteristics in different regions. This approach can result in over-processing in some areas while under-processing in others, creating inconsistent results.
AI Advantages and Capabilities
Content-Aware Processing: AI denoising systems analyze image content to understand what they're processing, applying different strategies to portraits, landscapes, technical subjects, and other content types. This intelligence enables more appropriate processing decisions that preserve the unique characteristics of different subject matter.
Learned Pattern Recognition: Through training on millions of images, AI systems develop sophisticated understanding of noise patterns and their relationship to legitimate image content. This learned knowledge enables more accurate discrimination between noise and detail than mathematical algorithms alone can achieve.
Adaptive Strength Control: Advanced AI systems automatically adjust processing strength based on local image characteristics, applying strong noise reduction in smooth areas while preserving detail in textured regions. This adaptive approach eliminates the need for manual parameter adjustment in most situations.
Hybrid Processing Approaches
Combined Methodologies: The most effective modern denoising solutions combine AI intelligence with traditional mathematical approaches, using each method's strengths for optimal results. AI provides content understanding and adaptive processing decisions, while traditional methods handle specific mathematical operations efficiently.
Preprocessing and Refinement: Some systems use traditional methods for initial noise reduction followed by AI refinement to restore details and correct artifacts. This approach can be more computationally efficient while still providing AI-enhanced results.
Professional Photography Applications {professional-photography-applications}
Wedding and Event Photography
Low-Light Challenges: Wedding photographers frequently work in challenging lighting conditions, from dimly lit churches to evening receptions with mixed lighting sources. These conditions necessitate high ISO settings that introduce significant noise, particularly in shadow areas of formal portraits and candid moments.
Workflow Efficiency: Professional wedding photographers may process hundreds or thousands of images from a single event. AI denoising tools that can batch process large image collections while maintaining consistent quality are essential for efficient workflow management. RestoreAI's Denoiser provides automated processing capabilities that maintain professional standards across entire wedding collections.
Client Expectations: Wedding clients expect flawless image quality regardless of shooting conditions. AI denoising enables photographers to deliver clean, professional results even from challenging situations that would have required significant manual retouching in the past.
Portrait Photography
Skin Texture Preservation: Portrait denoising requires particular attention to maintaining natural skin texture while removing unwanted noise. AI systems trained specifically on portrait photography understand the importance of preserving skin detail, pore structure, and natural texture variations that contribute to realistic skin rendering.
Hair and Fabric Details: Fine details in hair, clothing textures, and accessories require careful processing to avoid the plastic or artificial appearance that can result from aggressive noise reduction. Advanced AI algorithms recognize these texture types and apply appropriate processing to maintain natural appearance.
Professional Retouching Integration: AI denoising serves as an essential first step in professional portrait retouching workflows, providing clean base images that enable more effective subsequent editing. Clean, noise-free images require less manual spotting and allow retouchers to focus on creative enhancement rather than technical correction.
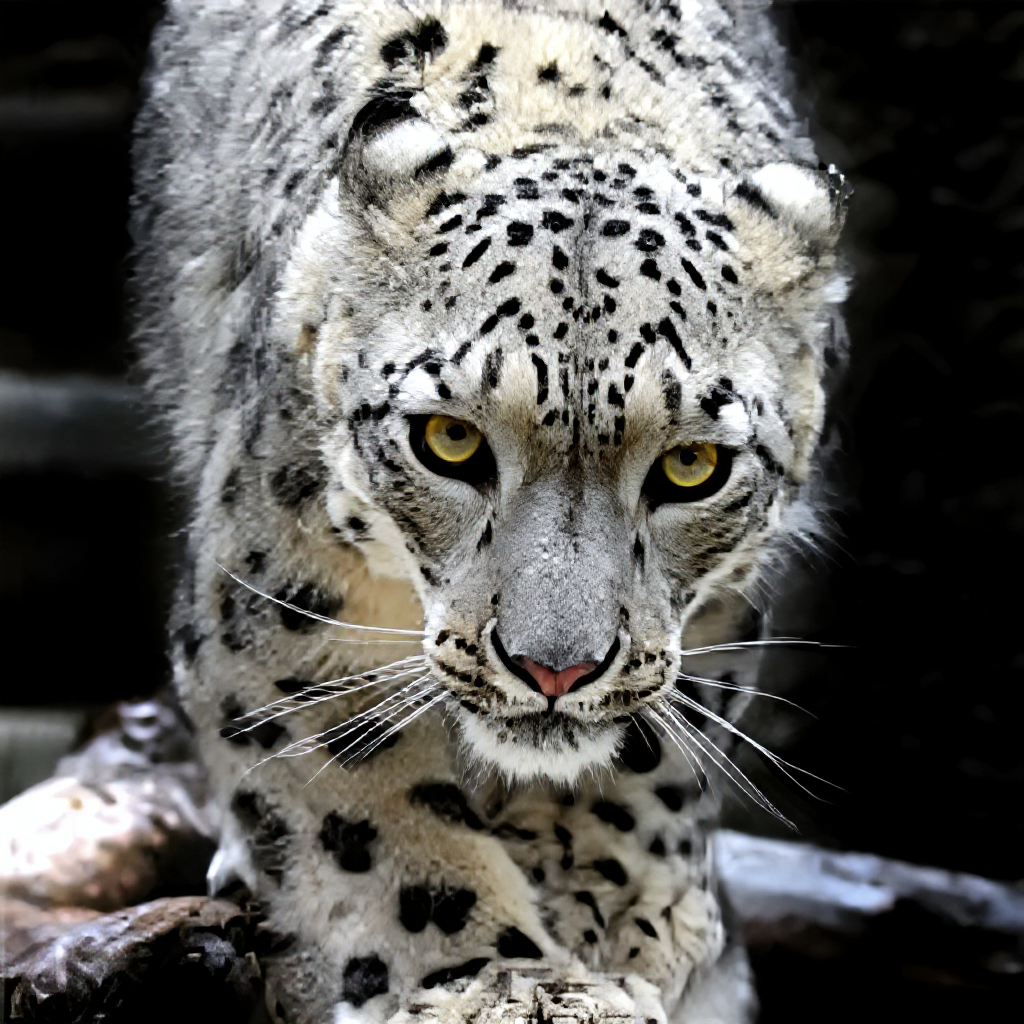
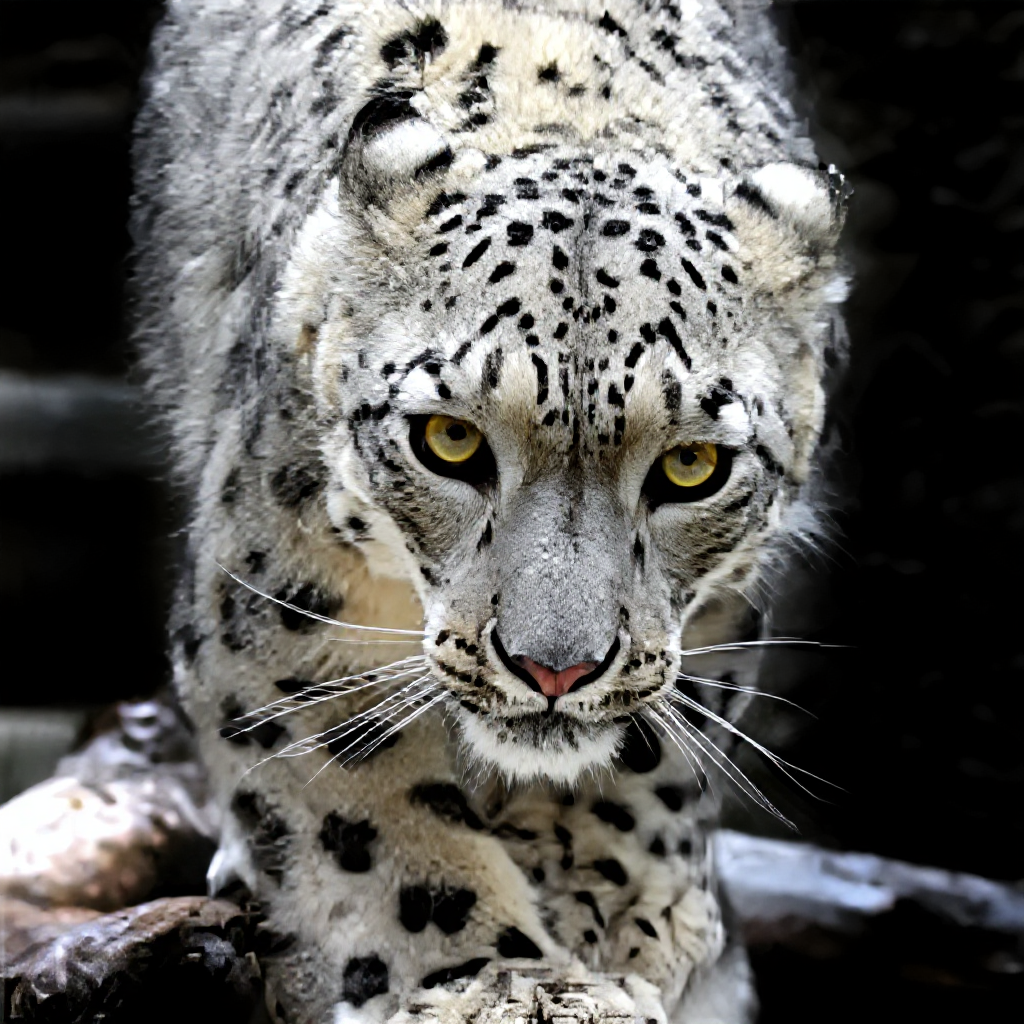
Wildlife and Nature Photography
Extreme Conditions: Wildlife photographers often work at the limits of camera capability, using long telephoto lenses in low light conditions that necessitate high ISO settings. The combination of challenging lighting and the need for fast shutter speeds to freeze animal movement creates demanding noise reduction requirements.
Fine Detail Preservation: Nature photography demands exceptional detail preservation, particularly for subjects like bird feathers, animal fur, and plant textures. AI denoising systems must maintain these crucial details while removing noise that could compromise the technical quality of wildlife images.
Environmental Considerations: Different natural environments present unique challenges for noise reduction. Forest canopies create dappled lighting with high contrast, while open landscapes may have uniform sky areas that require different processing approaches. AI systems that adapt to these varying conditions provide superior results.
Commercial and Product Photography
Technical Precision: Commercial photography requires exceptional technical quality, particularly for product images that will be used in advertising, catalogs, or e-commerce applications. Even minor noise artifacts can be problematic when images are closely examined or printed at large sizes.
Consistency Requirements: Commercial projects often require multiple images with consistent visual characteristics. AI denoising systems that provide repeatable results across similar lighting conditions help maintain the visual consistency essential for professional commercial work.
Brand Standards: Many commercial clients have specific technical standards for image quality, including noise levels and detail preservation requirements. AI denoising tools enable photographers to meet these standards consistently while maintaining efficient production workflows.
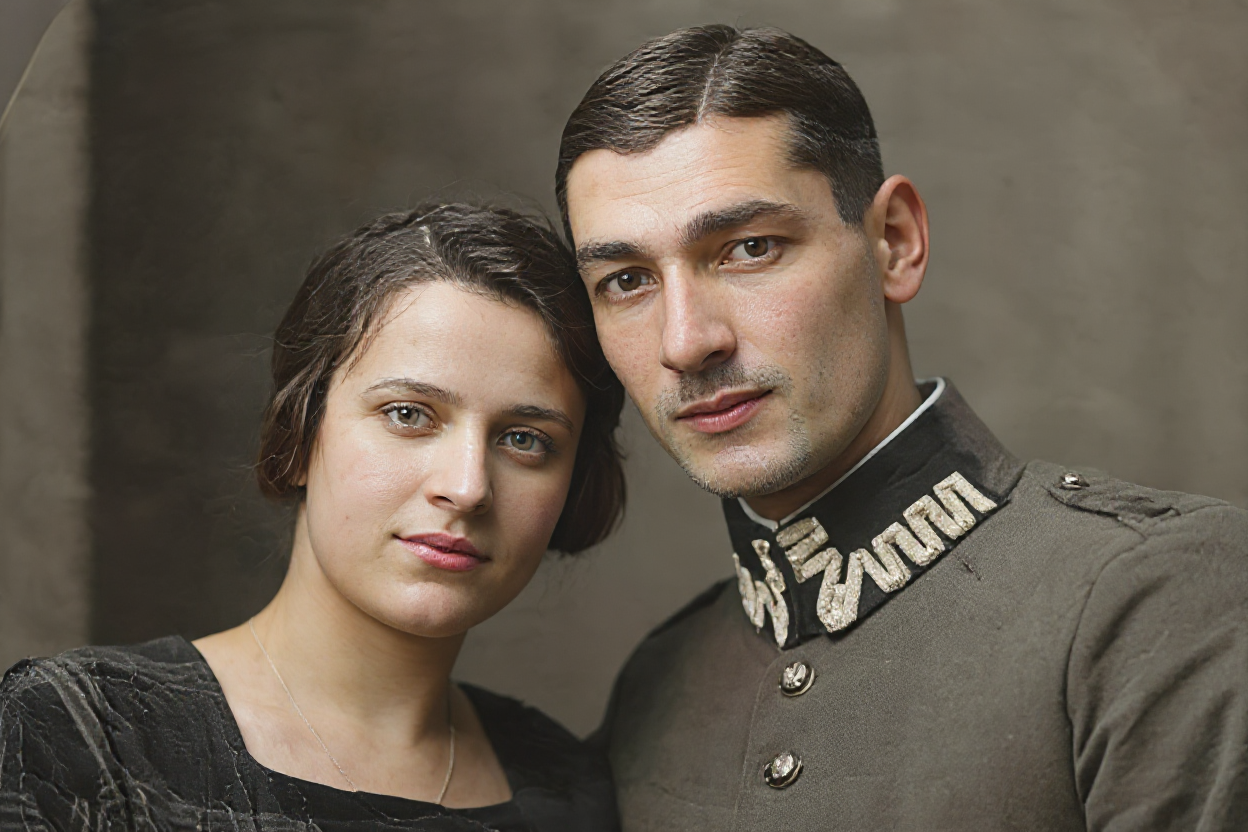
Documentary and Photojournalism
Authenticity Concerns: Documentary photographers must balance technical quality with authenticity concerns, ensuring that noise reduction doesn't alter the essential character or truthfulness of images. AI systems that preserve natural image characteristics while removing technical artifacts support ethical documentary practices.
Rapid Workflow Requirements: News and documentary photographers often work under tight deadlines that don't allow for extensive manual processing. Automated AI denoising that provides professional results without manual intervention is essential for meeting publication deadlines.
Archive Enhancement: Historical photojournalism archives can benefit from AI denoising to improve viewing quality for digital publication while preserving the essential character of historical images. This application requires careful balance between enhancement and historical accuracy.
Technical Implementation {technical-implementation}
Processing Pipeline Architecture
Multi-Stage Processing: Professional AI denoising implements multi-stage processing pipelines that address different aspects of noise reduction sequentially. Initial stages typically focus on obvious noise patterns, while later stages refine details and restore textures that may have been affected by earlier processing.
Quality Assessment Integration: Advanced systems include automated quality assessment that evaluates processing results and adjusts parameters if necessary. This feedback mechanism helps ensure consistent results across varying image conditions and content types.
Memory and Performance Optimization: Processing high-resolution images requires efficient memory management and computational optimization. Modern AI denoising systems use techniques like tile-based processing and progressive refinement to handle large images efficiently while maintaining quality.
Hardware Acceleration
GPU Processing: AI denoising benefits significantly from GPU acceleration, which can reduce processing times from minutes to seconds for high-resolution images. Professional workflows increasingly rely on dedicated GPU resources to enable real-time or near-real-time processing capabilities.
Cloud Processing Options: For photographers without dedicated processing hardware, cloud-based AI denoising provides access to powerful processing capabilities without local hardware investment. RestoreAI's cloud processing delivers professional results while scaling automatically to handle varying workload demands.
Mobile Implementation: Smartphone photography applications increasingly incorporate AI denoising capabilities for real-time processing during image capture. These implementations require optimization for mobile processors while still providing meaningful quality improvements.
Format Support and Workflow Integration
RAW Format Processing: Professional AI denoising systems support native RAW format processing, enabling noise reduction to be applied to unprocessed sensor data for optimal results. This approach provides better quality than processing JPEG or other compressed formats.
Color Space Management: Proper color space handling ensures that denoising processing doesn't introduce color shifts or tonal variations. Professional systems maintain color accuracy throughout the processing pipeline while supporting various color spaces and gamma curves.
Metadata Preservation: Professional workflows require preservation of image metadata including EXIF information, color profiles, and custom annotations. Quality AI denoising systems maintain this information while adding appropriate processing documentation.
Best Practices and Workflows {best-practices-and-workflows}
Optimal Shooting Techniques
ETTR (Expose to the Right): Exposing images to place highlights near the right edge of the histogram provides the best signal-to-noise ratio for shadows when processing. This technique minimizes noise in shadow areas where it's most visible and provides more flexibility during post-processing noise reduction.
ISO Strategy: Understanding your camera's ISO performance characteristics helps optimize the balance between shooting settings and post-processing noise reduction. Some cameras perform better with slight underexposure at lower ISO followed by brightening in post, while others benefit from optimal exposure at higher ISO settings.
Format Selection: Shooting in RAW format provides maximum flexibility for noise reduction processing, as it preserves the original sensor data without compression or processing artifacts. This approach enables more effective AI denoising compared to processing JPEG files.
Processing Workflow Integration
Early Pipeline Processing: Applying AI denoising early in the processing pipeline, before other adjustments like exposure correction or color grading, typically provides better results. This approach prevents noise amplification that can occur when adjusting underexposed images.
Selective Application: Different image regions may benefit from different noise reduction approaches. Professional workflows often incorporate masking techniques to apply varying levels of noise reduction to different image areas based on content and noise characteristics.
Quality Control Checkpoints: Establishing quality control checkpoints throughout the processing workflow helps ensure consistent results and catch any processing artifacts before final output. This is particularly important when batch processing large image collections.
Client Communication and Delivery
Expectation Management: Educating clients about noise reduction capabilities and limitations helps set appropriate expectations. While AI denoising can dramatically improve image quality, it's important to communicate any limitations, particularly for severely degraded source material.
Before/After Documentation: Providing before/after examples helps clients understand the value of AI denoising services and can justify premium pricing for enhanced processing. This documentation also serves as a portfolio element demonstrating technical capabilities.
Archival Considerations: Maintaining both original and processed versions of important images ensures flexibility for future reprocessing as technology improves. This approach is particularly important for valuable historical or irreplaceable images.
Batch Processing Strategies
Consistent Lighting Conditions: Images shot under similar lighting conditions can often be processed with identical settings, enabling efficient batch processing. Grouping images by shooting conditions optimizes processing efficiency while maintaining quality.
Progressive Enhancement: For large collections, applying initial automated processing followed by selective manual refinement provides an efficient balance between quality and productivity. This approach focuses manual attention on the most important images.
Quality Monitoring: When batch processing large collections, implementing sampling and quality monitoring helps catch any systematic issues before processing entire collections. Regular quality checks ensure consistent results across the entire batch.
Future of AI Denoising {future-of-ai-denoising}
Emerging Technologies
Real-Time Processing: Future AI denoising systems will increasingly operate in real-time during image capture, providing immediate feedback and eliminating post-processing requirements for many applications. This advancement will be particularly valuable for video applications and live streaming.
Multi-Frame Processing: Advanced systems will analyze multiple frames from video or burst photography to improve noise reduction quality. By combining information from several images, these systems can achieve superior results compared to single-frame processing.
Specialized Training: Future AI systems will likely include specialized training for specific photography genres, camera models, or even individual photographer styles. This specialization will enable more tailored processing that better meets specific professional requirements.
Integration Capabilities
Camera Integration: Future cameras may include built-in AI denoising capabilities that operate during image capture, providing clean images without requiring post-processing. This integration will democratize access to professional-quality noise reduction.
Cloud Connectivity: Enhanced cloud integration will enable photographers to access the latest AI denoising capabilities without local hardware limitations. This approach will also enable continuous improvement as AI systems are updated and refined.
Workflow Automation: Future systems will provide more sophisticated automation capabilities, learning individual photographer preferences and automatically applying appropriate processing based on image content and shooting conditions.
Quality Improvements
Detail Preservation: Ongoing research continues to improve the balance between noise reduction and detail preservation, with future systems expected to achieve even better results in challenging situations like extreme low-light photography.
Artifact Reduction: Future AI systems will better avoid processing artifacts that can appear with current technology, providing more natural-looking results that require less manual correction.
Content Understanding: Enhanced AI systems will develop better understanding of image content, enabling more intelligent processing decisions based on subject matter, intended use, and artistic intent.
AI denoising technology has revolutionized noise reduction in digital photography, providing capabilities that exceed traditional methods while maintaining natural image characteristics. Professional photographers across all genres now rely on AI denoising to deliver client expectations while maintaining efficient workflows.
RestoreAI's Denoiser tool represents the current state-of-the-art in AI denoising technology, providing professional-quality results for everything from wedding photography to commercial applications. The combination of advanced algorithms, efficient processing, and user-friendly interface makes it an essential tool for modern digital photography workflows.
For photographers seeking to improve their noise reduction capabilities, AI denoising offers immediate benefits in image quality, workflow efficiency, and client satisfaction. As the technology continues to evolve, these benefits will only become more pronounced, making AI denoising an increasingly important component of professional photography practice.
Whether you're dealing with challenging low-light conditions, high-ISO requirements, or legacy images requiring restoration, AI denoising technology provides the tools necessary to achieve professional results while maintaining the natural characteristics that make photographs compelling and authentic.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Digital Noise and Grain
2. The Science Behind AI Denoising
3. Types of Image Noise
4. AI vs Traditional Denoising Methods
5. Professional Photography Applications
6. Technical Implementation
7. Best Practices and Workflows
8. Future of AI Denoising
Digital noise and grain represent one of photography's most persistent challenges, affecting image quality across all genres of photography. From wedding photographers working in dimly lit venues to wildlife photographers capturing subjects in challenging lighting conditions, unwanted noise can compromise the technical and aesthetic quality of images. AI-powered denoising technology has revolutionized how photographers approach noise reduction, offering unprecedented capability to remove unwanted artifacts while preserving critical image details that traditional methods often sacrifice.
The emergence of artificial intelligence in image processing has fundamentally changed the denoising landscape. Where conventional algorithms rely on mathematical interpolation and statistical analysis, AI denoising systems learn from millions of image examples to understand the complex relationship between noise patterns and legitimate image content. This learning-based approach enables more intelligent decision-making about what constitutes noise versus essential image information.
Understanding Digital Noise and Grain {understanding-digital-noise-and-grain}
The Physics of Digital Noise
Digital noise originates from multiple sources within the imaging chain, each contributing different characteristics to the final image degradation. Thermal noise occurs when electrons move randomly within the camera sensor due to heat, creating bright pixels that don't correspond to actual light exposure. This type of noise increases significantly with higher sensor temperatures, which is why long exposures and high-performance cameras often include active cooling systems.
Shot noise represents a fundamental physical limitation based on the quantum nature of light itself. When photons strike the sensor, they arrive randomly rather than in a steady stream, creating statistical variations in the signal. This randomness becomes more apparent in low-light conditions where fewer photons are available to create a stable signal, resulting in visible noise patterns.
Read noise occurs during the electronic conversion of photon-generated charges into digital values. This process inherently introduces small electrical variations that manifest as noise, particularly visible in shadow areas where the actual signal is weak. Modern sensor designs continuously work to minimize read noise through improved electronics and processing techniques.
ISO Performance and Noise Characteristics
Modern Sensor Technology: Contemporary camera sensors demonstrate remarkable improvements in high-ISO performance compared to previous generations. Full-frame sensors generally exhibit superior noise characteristics due to larger individual photosite areas that can capture more light. However, even the most advanced sensors show increased noise at elevated ISO settings.
Sensor Size Impact: The relationship between sensor size and noise performance is fundamental to understanding when denoising becomes necessary. Larger sensors can maintain better signal-to-noise ratios because individual photosites have more surface area to collect light. This is why full-frame cameras typically outperform crop sensors in low-light conditions.
ISO Invariance: Some modern cameras exhibit ISO invariance, meaning similar noise levels can be achieved by underexposing at lower ISO settings and brightening in post-processing versus shooting at higher ISO values. Understanding your camera's ISO performance helps optimize the balance between in-camera settings and post-processing denoising.
Film Grain vs Digital Noise
Aesthetic Differences: Film grain possesses organic, random characteristics that many photographers find aesthetically pleasing. Unlike digital noise, which tends to create regular patterns and color speckles, film grain maintains a more natural, textured appearance. However, when digitizing film photographs, this grain can sometimes interfere with modern viewing and printing requirements.
Preservation Considerations: When working with scanned film photographs, photographers must decide whether to preserve the original grain character or remove it for cleaner presentation. RestoreAI's Denoiser includes specific algorithms trained to distinguish between desirable film grain and unwanted digital artifacts, allowing selective treatment of different noise types.
The Science Behind AI Denoising {the-science-behind-ai-denoising}
Deep Learning Architecture
Convolutional Neural Networks: Modern AI denoising relies primarily on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) that excel at recognizing spatial patterns in image data. These networks learn to identify noise patterns by analyzing millions of image pairs showing the same content with and without noise. The learning process enables the AI to understand complex relationships between noise characteristics and legitimate image features.
Attention Mechanisms: Advanced denoising networks incorporate attention mechanisms that help the AI focus on specific image regions requiring different treatment. These mechanisms allow the system to apply stronger noise reduction in smooth areas like skies while preserving fine details in textured regions like fabric or foliage.
Multi-Scale Processing: Professional AI denoising systems analyze images at multiple resolution scales simultaneously. This approach enables detection of both fine-grained noise patterns and larger structural features that should be preserved during the denoising process.
Training Methodologies
Synthetic Noise Generation: AI denoising networks are trained using millions of high-quality images to which various types of synthetic noise are added. This approach allows the system to learn noise characteristics without requiring paired clean/noisy versions of real photographs. The synthetic noise must accurately represent real-world noise patterns to ensure effective performance.
Real-World Data Integration: The most effective AI denoising systems supplement synthetic training data with real-world noisy images captured under various conditions. This combined approach helps the AI generalize better to actual photography scenarios rather than only laboratory-generated noise patterns.
Transfer Learning: Modern AI denoising development leverages transfer learning, where networks initially trained on general image recognition tasks are fine-tuned specifically for noise removal. This approach accelerates training and often produces superior results compared to training from scratch.
Edge Preservation Technology
Gradient Analysis: AI denoising systems must distinguish between noise and legitimate edges in images. Advanced algorithms analyze local gradients to identify areas where intensity changes represent actual image content versus random noise variations. This analysis enables selective processing that preserves important edges while removing unwanted artifacts.
Texture Recognition: Sophisticated AI denoising recognizes different texture types and applies appropriate processing to each. Smooth gradients receive aggressive noise reduction, while textured areas like fabric, bark, or grass maintain their characteristic patterns without being smoothed away.
Adaptive Processing: The most advanced systems adapt their processing strategy based on local image content. Areas containing faces might receive different treatment than landscapes, and technical subjects like electronics or machinery might be processed differently than organic subjects.
Types of Image Noise {types-of-image-noise}
Luminance Noise
Characteristics and Detection: Luminance noise appears as random brightness variations across the image, creating a speckled or grainy appearance particularly visible in uniform areas like skies or walls. This type of noise is most apparent in shadow areas where the signal-to-noise ratio is lowest. AI algorithms detect luminance noise by analyzing statistical variations in pixel brightness values across similar image regions.
Impact on Image Quality: Luminance noise primarily affects the perceived sharpness and smoothness of images. While generally less objectionable than color noise, excessive luminance noise can make images appear gritty and unprofessional. In commercial photography, even moderate luminance noise can be problematic for large-format printing or detailed inspection.
Processing Strategies: AI denoising systems use sophisticated edge detection to apply luminance noise reduction selectively. Smooth areas receive aggressive processing while textured regions maintain their detail structure. The challenge lies in distinguishing between noise and legitimate fine detail, particularly in subjects like fabric textures or natural surfaces.
Color Noise (Chroma Noise)
Visual Characteristics: Color noise manifests as random color speckles or shifts that don't correspond to actual subject colors. This type of noise is particularly problematic because it creates unrealistic color variations that immediately appear unnatural to viewers. Color noise often exhibits characteristic patterns specific to individual camera models and sensor designs.
Technical Causes: Color noise typically results from imperfections in the color filter array or differences in sensitivity between color channels. High ISO settings amplify these variations, creating visible color artifacts. Digital processing algorithms within cameras sometimes contribute additional color noise during the conversion from RAW sensor data to processed images.
AI Solutions: Advanced AI denoising systems analyze color relationships across the image to identify and correct inappropriate color variations. These algorithms learn normal color patterns for different subject types, enabling intelligent correction of color noise while preserving legitimate color variations and gradients.
Pattern Noise and Fixed-Pattern Artifacts
Source and Characteristics: Pattern noise appears as regular or semi-regular patterns across the image, often resulting from electrical interference or sensor manufacturing variations. Unlike random noise, pattern noise exhibits consistent characteristics that can sometimes be more distracting than purely random artifacts.
Hot Pixels and Dead Pixels: Long exposures can reveal hot pixels that consistently produce bright spots, while dead pixels fail to respond to light at all. AI denoising systems can learn to identify and correct these fixed-pattern artifacts by analyzing pixel behavior across multiple images or using statistical analysis of surrounding pixels.
Banding and Striping: Some cameras exhibit banding patterns, particularly in shadow areas or during high-ISO shooting. These patterns result from variations in sensor readout electronics and can be particularly challenging to correct without affecting legitimate image content. AI systems trained specifically on these patterns can often provide effective correction.
Compression Artifacts
JPEG Compression Effects: While not technically noise, JPEG compression creates artifacts that share similar characteristics with noise and often require similar correction approaches. These artifacts include blocking patterns, ringing around edges, and color bleeding between adjacent areas.
AI Enhancement Integration: Modern AI denoising tools often include specialized algorithms for correcting compression artifacts alongside traditional noise reduction. This integrated approach is particularly valuable when working with images that have undergone multiple compression cycles or aggressive compression settings.
AI vs Traditional Denoising Methods {ai-vs-traditional-denoising-methods}
Limitations of Traditional Approaches
Statistical Filtering: Traditional denoising relies heavily on statistical analysis of pixel neighborhoods, applying mathematical filters that assume noise characteristics follow predictable patterns. While effective for simple noise types, these methods often struggle with complex real-world noise that varies across the image or exhibits non-standard characteristics.
Edge Preservation Challenges: Conventional algorithms face fundamental difficulties in distinguishing between noise and legitimate image details. Aggressive noise reduction often results in over-smoothing that eliminates fine textures and reduces apparent sharpness. Conservative settings may leave visible noise artifacts that compromise image quality.
One-Size-Fits-All Processing: Traditional methods typically apply uniform processing across the entire image, failing to account for varying noise characteristics in different regions. This approach can result in over-processing in some areas while under-processing in others, creating inconsistent results.
AI Advantages and Capabilities
Content-Aware Processing: AI denoising systems analyze image content to understand what they're processing, applying different strategies to portraits, landscapes, technical subjects, and other content types. This intelligence enables more appropriate processing decisions that preserve the unique characteristics of different subject matter.
Learned Pattern Recognition: Through training on millions of images, AI systems develop sophisticated understanding of noise patterns and their relationship to legitimate image content. This learned knowledge enables more accurate discrimination between noise and detail than mathematical algorithms alone can achieve.
Adaptive Strength Control: Advanced AI systems automatically adjust processing strength based on local image characteristics, applying strong noise reduction in smooth areas while preserving detail in textured regions. This adaptive approach eliminates the need for manual parameter adjustment in most situations.
Hybrid Processing Approaches
Combined Methodologies: The most effective modern denoising solutions combine AI intelligence with traditional mathematical approaches, using each method's strengths for optimal results. AI provides content understanding and adaptive processing decisions, while traditional methods handle specific mathematical operations efficiently.
Preprocessing and Refinement: Some systems use traditional methods for initial noise reduction followed by AI refinement to restore details and correct artifacts. This approach can be more computationally efficient while still providing AI-enhanced results.
Professional Photography Applications {professional-photography-applications}
Wedding and Event Photography
Low-Light Challenges: Wedding photographers frequently work in challenging lighting conditions, from dimly lit churches to evening receptions with mixed lighting sources. These conditions necessitate high ISO settings that introduce significant noise, particularly in shadow areas of formal portraits and candid moments.
Workflow Efficiency: Professional wedding photographers may process hundreds or thousands of images from a single event. AI denoising tools that can batch process large image collections while maintaining consistent quality are essential for efficient workflow management. RestoreAI's Denoiser provides automated processing capabilities that maintain professional standards across entire wedding collections.
Client Expectations: Wedding clients expect flawless image quality regardless of shooting conditions. AI denoising enables photographers to deliver clean, professional results even from challenging situations that would have required significant manual retouching in the past.
Portrait Photography
Skin Texture Preservation: Portrait denoising requires particular attention to maintaining natural skin texture while removing unwanted noise. AI systems trained specifically on portrait photography understand the importance of preserving skin detail, pore structure, and natural texture variations that contribute to realistic skin rendering.
Hair and Fabric Details: Fine details in hair, clothing textures, and accessories require careful processing to avoid the plastic or artificial appearance that can result from aggressive noise reduction. Advanced AI algorithms recognize these texture types and apply appropriate processing to maintain natural appearance.
Professional Retouching Integration: AI denoising serves as an essential first step in professional portrait retouching workflows, providing clean base images that enable more effective subsequent editing. Clean, noise-free images require less manual spotting and allow retouchers to focus on creative enhancement rather than technical correction.
Wildlife and Nature Photography
Extreme Conditions: Wildlife photographers often work at the limits of camera capability, using long telephoto lenses in low light conditions that necessitate high ISO settings. The combination of challenging lighting and the need for fast shutter speeds to freeze animal movement creates demanding noise reduction requirements.
Fine Detail Preservation: Nature photography demands exceptional detail preservation, particularly for subjects like bird feathers, animal fur, and plant textures. AI denoising systems must maintain these crucial details while removing noise that could compromise the technical quality of wildlife images.
Environmental Considerations: Different natural environments present unique challenges for noise reduction. Forest canopies create dappled lighting with high contrast, while open landscapes may have uniform sky areas that require different processing approaches. AI systems that adapt to these varying conditions provide superior results.
Commercial and Product Photography
Technical Precision: Commercial photography requires exceptional technical quality, particularly for product images that will be used in advertising, catalogs, or e-commerce applications. Even minor noise artifacts can be problematic when images are closely examined or printed at large sizes.
Consistency Requirements: Commercial projects often require multiple images with consistent visual characteristics. AI denoising systems that provide repeatable results across similar lighting conditions help maintain the visual consistency essential for professional commercial work.
Brand Standards: Many commercial clients have specific technical standards for image quality, including noise levels and detail preservation requirements. AI denoising tools enable photographers to meet these standards consistently while maintaining efficient production workflows.
Documentary and Photojournalism
Authenticity Concerns: Documentary photographers must balance technical quality with authenticity concerns, ensuring that noise reduction doesn't alter the essential character or truthfulness of images. AI systems that preserve natural image characteristics while removing technical artifacts support ethical documentary practices.
Rapid Workflow Requirements: News and documentary photographers often work under tight deadlines that don't allow for extensive manual processing. Automated AI denoising that provides professional results without manual intervention is essential for meeting publication deadlines.
Archive Enhancement: Historical photojournalism archives can benefit from AI denoising to improve viewing quality for digital publication while preserving the essential character of historical images. This application requires careful balance between enhancement and historical accuracy.
Technical Implementation {technical-implementation}
Processing Pipeline Architecture
Multi-Stage Processing: Professional AI denoising implements multi-stage processing pipelines that address different aspects of noise reduction sequentially. Initial stages typically focus on obvious noise patterns, while later stages refine details and restore textures that may have been affected by earlier processing.
Quality Assessment Integration: Advanced systems include automated quality assessment that evaluates processing results and adjusts parameters if necessary. This feedback mechanism helps ensure consistent results across varying image conditions and content types.
Memory and Performance Optimization: Processing high-resolution images requires efficient memory management and computational optimization. Modern AI denoising systems use techniques like tile-based processing and progressive refinement to handle large images efficiently while maintaining quality.
Hardware Acceleration
GPU Processing: AI denoising benefits significantly from GPU acceleration, which can reduce processing times from minutes to seconds for high-resolution images. Professional workflows increasingly rely on dedicated GPU resources to enable real-time or near-real-time processing capabilities.
Cloud Processing Options: For photographers without dedicated processing hardware, cloud-based AI denoising provides access to powerful processing capabilities without local hardware investment. RestoreAI's cloud processing delivers professional results while scaling automatically to handle varying workload demands.
Mobile Implementation: Smartphone photography applications increasingly incorporate AI denoising capabilities for real-time processing during image capture. These implementations require optimization for mobile processors while still providing meaningful quality improvements.
Format Support and Workflow Integration
RAW Format Processing: Professional AI denoising systems support native RAW format processing, enabling noise reduction to be applied to unprocessed sensor data for optimal results. This approach provides better quality than processing JPEG or other compressed formats.
Color Space Management: Proper color space handling ensures that denoising processing doesn't introduce color shifts or tonal variations. Professional systems maintain color accuracy throughout the processing pipeline while supporting various color spaces and gamma curves.
Metadata Preservation: Professional workflows require preservation of image metadata including EXIF information, color profiles, and custom annotations. Quality AI denoising systems maintain this information while adding appropriate processing documentation.
Best Practices and Workflows {best-practices-and-workflows}
Optimal Shooting Techniques
ETTR (Expose to the Right): Exposing images to place highlights near the right edge of the histogram provides the best signal-to-noise ratio for shadows when processing. This technique minimizes noise in shadow areas where it's most visible and provides more flexibility during post-processing noise reduction.
ISO Strategy: Understanding your camera's ISO performance characteristics helps optimize the balance between shooting settings and post-processing noise reduction. Some cameras perform better with slight underexposure at lower ISO followed by brightening in post, while others benefit from optimal exposure at higher ISO settings.
Format Selection: Shooting in RAW format provides maximum flexibility for noise reduction processing, as it preserves the original sensor data without compression or processing artifacts. This approach enables more effective AI denoising compared to processing JPEG files.
Processing Workflow Integration
Early Pipeline Processing: Applying AI denoising early in the processing pipeline, before other adjustments like exposure correction or color grading, typically provides better results. This approach prevents noise amplification that can occur when adjusting underexposed images.
Selective Application: Different image regions may benefit from different noise reduction approaches. Professional workflows often incorporate masking techniques to apply varying levels of noise reduction to different image areas based on content and noise characteristics.
Quality Control Checkpoints: Establishing quality control checkpoints throughout the processing workflow helps ensure consistent results and catch any processing artifacts before final output. This is particularly important when batch processing large image collections.
Client Communication and Delivery
Expectation Management: Educating clients about noise reduction capabilities and limitations helps set appropriate expectations. While AI denoising can dramatically improve image quality, it's important to communicate any limitations, particularly for severely degraded source material.
Before/After Documentation: Providing before/after examples helps clients understand the value of AI denoising services and can justify premium pricing for enhanced processing. This documentation also serves as a portfolio element demonstrating technical capabilities.
Archival Considerations: Maintaining both original and processed versions of important images ensures flexibility for future reprocessing as technology improves. This approach is particularly important for valuable historical or irreplaceable images.
Batch Processing Strategies
Consistent Lighting Conditions: Images shot under similar lighting conditions can often be processed with identical settings, enabling efficient batch processing. Grouping images by shooting conditions optimizes processing efficiency while maintaining quality.
Progressive Enhancement: For large collections, applying initial automated processing followed by selective manual refinement provides an efficient balance between quality and productivity. This approach focuses manual attention on the most important images.
Quality Monitoring: When batch processing large collections, implementing sampling and quality monitoring helps catch any systematic issues before processing entire collections. Regular quality checks ensure consistent results across the entire batch.
Future of AI Denoising {future-of-ai-denoising}
Emerging Technologies
Real-Time Processing: Future AI denoising systems will increasingly operate in real-time during image capture, providing immediate feedback and eliminating post-processing requirements for many applications. This advancement will be particularly valuable for video applications and live streaming.
Multi-Frame Processing: Advanced systems will analyze multiple frames from video or burst photography to improve noise reduction quality. By combining information from several images, these systems can achieve superior results compared to single-frame processing.
Specialized Training: Future AI systems will likely include specialized training for specific photography genres, camera models, or even individual photographer styles. This specialization will enable more tailored processing that better meets specific professional requirements.
Integration Capabilities
Camera Integration: Future cameras may include built-in AI denoising capabilities that operate during image capture, providing clean images without requiring post-processing. This integration will democratize access to professional-quality noise reduction.
Cloud Connectivity: Enhanced cloud integration will enable photographers to access the latest AI denoising capabilities without local hardware limitations. This approach will also enable continuous improvement as AI systems are updated and refined.
Workflow Automation: Future systems will provide more sophisticated automation capabilities, learning individual photographer preferences and automatically applying appropriate processing based on image content and shooting conditions.
Quality Improvements
Detail Preservation: Ongoing research continues to improve the balance between noise reduction and detail preservation, with future systems expected to achieve even better results in challenging situations like extreme low-light photography.
Artifact Reduction: Future AI systems will better avoid processing artifacts that can appear with current technology, providing more natural-looking results that require less manual correction.
Content Understanding: Enhanced AI systems will develop better understanding of image content, enabling more intelligent processing decisions based on subject matter, intended use, and artistic intent.
AI denoising technology has revolutionized noise reduction in digital photography, providing capabilities that exceed traditional methods while maintaining natural image characteristics. Professional photographers across all genres now rely on AI denoising to deliver client expectations while maintaining efficient workflows.
RestoreAI's Denoiser tool represents the current state-of-the-art in AI denoising technology, providing professional-quality results for everything from wedding photography to commercial applications. The combination of advanced algorithms, efficient processing, and user-friendly interface makes it an essential tool for modern digital photography workflows.
For photographers seeking to improve their noise reduction capabilities, AI denoising offers immediate benefits in image quality, workflow efficiency, and client satisfaction. As the technology continues to evolve, these benefits will only become more pronounced, making AI denoising an increasingly important component of professional photography practice.
Whether you're dealing with challenging low-light conditions, high-ISO requirements, or legacy images requiring restoration, AI denoising technology provides the tools necessary to achieve professional results while maintaining the natural characteristics that make photographs compelling and authentic.