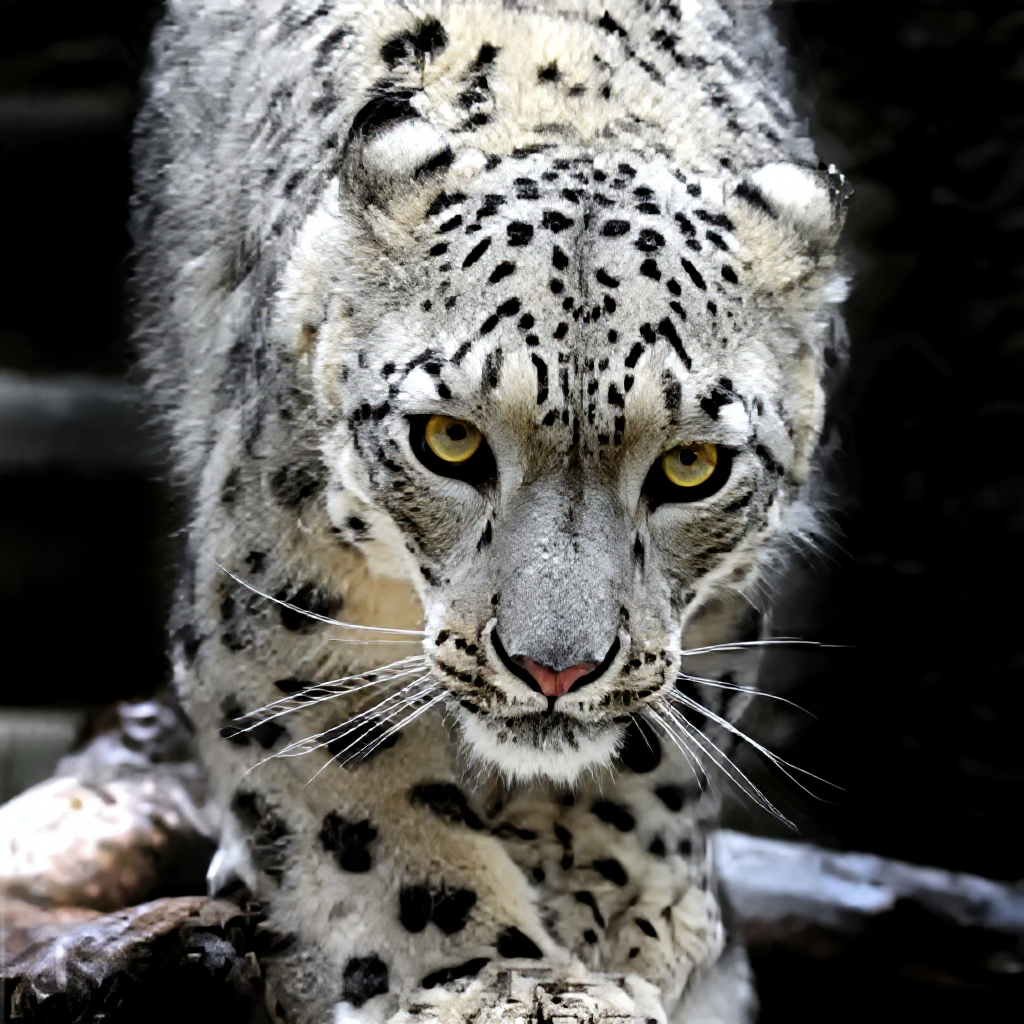
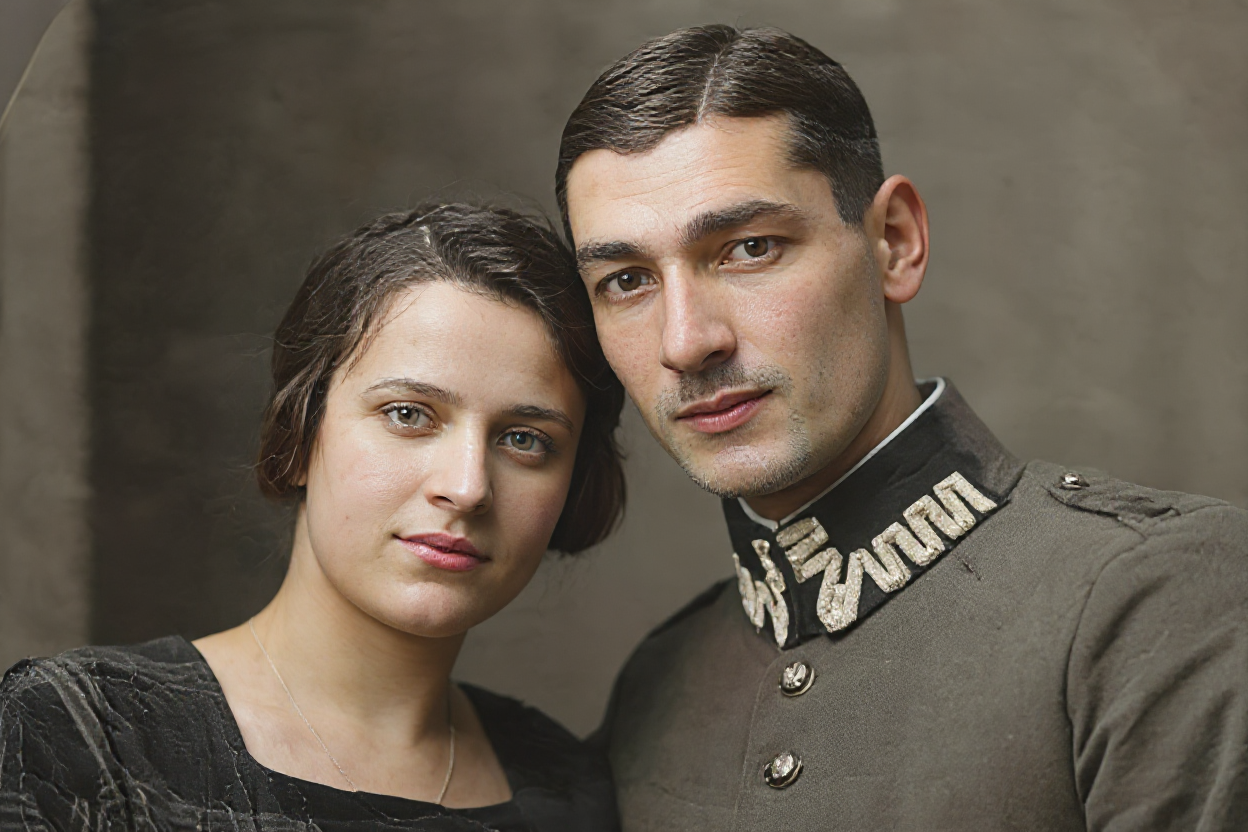
Low Quality Photo Enhancement: Transform Pixelated Images into HD
In the digital age, we're constantly dealing with images of varying quality. From heavily compressed social media uploads to low-resolution screenshots, poor-quality images are everywhere. However, 2025's advanced AI technology has revolutionized our ability to transform these seemingly unusable images into stunning, high-definition masterpieces.
This comprehensive guide explores the cutting-edge world of AI-powered low-quality photo enhancement, revealing how modern algorithms can breathe new life into pixelated, compressed, and degraded images. Whether you're dealing with family photos damaged by compression, low-resolution graphics that need upgrading, or any image suffering from quality issues, AI enhancement offers unprecedented solutions.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Low-Quality Image Problems
2. The Science of AI Quality Enhancement
3. Types of Quality Degradation AI Can Fix
4. Advanced Enhancement Algorithms
5. Professional Workflow Applications
6. Industry-Specific Use Cases
7. Technical Implementation Strategies
8. Future Developments in Quality Enhancement
Understanding Low-Quality Image Problems
The Nature of Digital Image Degradation
Digital images can suffer from quality loss through various mechanisms, each requiring different enhancement approaches. Understanding these degradation types is crucial for effective enhancement.
Compression Artifacts: When images are compressed for storage or transmission, data is lost, creating visible artifacts like blockiness, ringing, and color banding. JPEG compression, while efficient, introduces specific patterns of degradation that affect image quality.
Resolution Limitations: Low-resolution images lack the pixel density needed for sharp, detailed reproduction. This limitation becomes particularly problematic when images need to be displayed at larger sizes or higher resolutions.
Bit Depth Reduction: Color quantization reduces the number of available colors, creating posterization effects and loss of smooth gradations.
Sampling Issues: Poor sampling during image capture or conversion can introduce aliasing, moiré patterns, and other artifacts that degrade visual quality.
Sources of Image Quality Loss
Digital Camera Limitations: Early digital cameras, smartphone cameras, and budget imaging devices often produce images with inherent quality limitations due to sensor size, processing power, and lens quality constraints.
File Format Constraints: Aggressive compression settings in formats like JPEG can severely impact image quality, especially after multiple save operations.
Display and Capture Limitations: Screenshots from low-resolution displays, scanned images from poor-quality scanners, and images captured from video sources often suffer from quality issues.
Network Transmission: Images shared through social media platforms, messaging apps, and email systems are often automatically compressed, reducing quality significantly.
Historical Technology: Images created or processed with older technology may have quality limitations that modern enhancement can address.
The Science of AI Quality Enhancement
Deep Learning Approaches to Quality Improvement
Modern AI quality enhancement relies on sophisticated neural networks trained on massive datasets of high and low-quality image pairs. These systems learn to understand the relationship between degraded and pristine images, enabling them to make intelligent enhancement decisions.
Super-Resolution Networks: These specialized AI models can generate high-resolution details from low-resolution inputs by learning patterns and textures from training data. Unlike simple interpolation, these networks can create realistic detail that wasn't present in the original image.
Artifact Removal Networks: Dedicated AI systems trained specifically to identify and remove compression artifacts, noise, and other quality issues while preserving important image content.
Multi-Scale Processing: Advanced algorithms process images at multiple resolution levels simultaneously, ensuring consistent enhancement across different scales of detail.
Perceptual Loss Functions: Modern training approaches use perceptual similarity measures rather than simple pixel-wise comparisons, resulting in enhancements that look more natural to human viewers.
Computational Techniques
Residual Learning: Advanced network architectures that learn to predict the difference between low and high-quality images, enabling more effective training and better results.
Attention Mechanisms: AI systems that can focus on the most important areas of an image, applying stronger enhancement where it's needed most.
Progressive Enhancement: Multi-stage approaches that gradually improve image quality through successive refinement steps.
Domain Adaptation: Techniques that allow AI models trained on one type of image to work effectively on different types of content.
Types of Quality Degradation AI Can Fix
Compression-Related Issues
JPEG Blockiness: The characteristic 8x8 pixel blocks created by JPEG compression can be smoothed and eliminated while preserving important edge information.
Ringing Artifacts: Overshoot and undershoot artifacts around edges caused by compression can be identified and corrected.
Color Banding: Smooth color gradients broken into visible bands due to quantization can be restored to natural smoothness.
Mosquito Noise: High-frequency noise around edges and in textured areas can be reduced while maintaining detail clarity.
Resolution and Detail Issues
Pixelation: Blocky, pixelated images can be transformed into smooth, naturally detailed versions through intelligent interpolation and detail generation.
Jagged Edges: Aliasing and stair-stepping effects on diagonal lines and curves can be smoothed for more natural appearance.
Loss of Fine Detail: AI can reconstruct fine textures and details that were lost due to low resolution or poor capture quality.
Scale-Related Problems: Issues that arise when small images are displayed at larger sizes can be addressed through intelligent upscaling.
Color and Tonal Problems
Color Quantization: Reduced color palettes can be expanded to full color depth with natural-looking gradations.
Contrast Loss: Flat, low-contrast images can be enhanced to reveal hidden detail and improve visual impact.
Saturation Issues: Over-saturated or under-saturated colors can be corrected to more natural levels.
Gamma Problems: Incorrect gamma encoding can be detected and corrected for proper tonal reproduction.
Noise and Grain Issues
Digital Noise: Random pixel variations from sensor limitations or processing can be reduced while preserving image detail.
Compression Noise: Noise introduced by aggressive compression algorithms can be distinguished from image content and removed.
Scan Artifacts: Dust, scratches, and other artifacts from scanning processes can be identified and eliminated.
Film Grain: Excessive grain from high-ISO photography or film scanning can be reduced to appropriate levels.
Advanced AI Enhancement Algorithms
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs represent one of the most powerful approaches to image quality enhancement. These systems consist of two competing neural networks: a generator that creates enhanced images and a discriminator that evaluates their quality.
Enhanced SRGAN: Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks specifically designed for image upscaling and quality improvement.
Real-ESRGAN: Advanced versions trained on real-world degraded images rather than artificially degraded ones, providing better performance on actual low-quality photos.
Progressive Growing: GAN architectures that generate increasingly higher resolution images through successive stages.
Style Transfer GANs: Systems that can improve image quality while maintaining or enhancing artistic style.
Transformer-Based Approaches
Vision Transformers: Attention-based models that can understand global image context for more coherent enhancement decisions.
Swin Transformers: Hierarchical transformers that efficiently process images at multiple scales for comprehensive quality improvement.
Cross-Attention Mechanisms: Systems that can correlate information across different parts of an image for better enhancement consistency.
Hybrid Approaches
CNN-Transformer Hybrids: Combinations that leverage the local feature extraction of CNNs with the global understanding of transformers.
Multi-Task Learning: Systems trained simultaneously on multiple quality enhancement tasks for more robust performance.
Ensemble Methods: Combining multiple specialized models for optimal results across different types of degradation.
Professional Workflow Applications
Photography and Imaging Professionals
Print Preparation: Enhancing low-resolution images for large-format printing, enabling the use of images that would otherwise be unsuitable for print reproduction.
Archive Digitization: Improving the quality of digitized historical photographs, documents, and artwork for preservation and display purposes.
Client Deliverables: Enhancing images for professional delivery when original capture wasn't optimal due to circumstances or equipment limitations.
Stock Photography: Upgrading older stock images to modern quality standards for continued commercial viability.
Content Creation and Media
Social Media Optimization: Enhancing images that have been degraded by social platform compression for better visual impact.
Video Production: Improving still frames extracted from video for use in promotional materials and documentation.
Website Development: Enhancing images for web use, ensuring they look sharp across different devices and screen resolutions.
Digital Marketing: Improving image quality for advertising and promotional materials where high visual impact is crucial.
E-commerce and Retail
Product Photography: Enhancing product images that may have been captured with limited equipment or in challenging conditions.
Catalog Management: Upgrading existing product images to maintain consistent quality standards across large inventories.
Marketplace Optimization: Improving image quality for better performance on e-commerce platforms where visual quality affects sales.
Brand Consistency: Ensuring all brand imagery meets modern quality standards regardless of original capture conditions.
Using RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer
Comprehensive Enhancement Process
RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer tool provides state-of-the-art quality improvement through an intuitive, professional-grade interface:
Step 1: Image Analysis and Assessment
Upload your low-quality image and let the AI automatically analyze the types of degradation present, identifying specific issues like compression artifacts, pixelation, or noise.
Step 2: Intelligent Enhancement Selection
The AI determines the optimal enhancement strategies based on the specific quality issues detected, selecting appropriate algorithms for maximum improvement.
Step 3: Multi-Stage Processing
Images undergo sophisticated multi-stage enhancement, with different algorithms addressing specific quality issues in optimal sequence.
Step 4: Quality Optimization
The system fine-tunes enhancement parameters to achieve the best possible balance between quality improvement and natural appearance.
Step 5: Output Generation
Generate enhanced images in multiple resolutions and formats suitable for your specific use case.
Enhancement Customization Options
Artifact Reduction Strength: Control the aggressiveness of compression artifact removal to balance smoothness with detail preservation.
Detail Enhancement Level: Adjust how much fine detail the AI generates, allowing for subtle or dramatic improvements.
Color Restoration: Fine-tune color enhancement to achieve natural color reproduction or creative color grading.
Noise Reduction: Balance noise removal with detail preservation for optimal results in different viewing contexts.
Resolution Scaling: Choose output resolution based on intended use, from web display to large-format printing.
Industry-Specific Applications
Healthcare and Medical Imaging
Historical Medical Records: Enhancing old medical photographs and documentation for modern digital archives.
Telemedicine Support: Improving image quality for remote medical consultations where image clarity is crucial for diagnosis.
Educational Materials: Upgrading medical education imagery for modern display and learning systems.
Research Documentation: Enhancing historical medical research imagery for contemporary analysis and publication.
Legal and Forensic Applications
Evidence Enhancement: Improving the quality of photographic evidence while maintaining authenticity and legal admissibility.
Historical Document Processing: Enhancing scanned legal documents and photographs for better readability and preservation.
Surveillance Image Improvement: Upgrading security camera footage and images for better identification and analysis.
Court Presentation: Preparing enhanced images for clear courtroom display while maintaining evidentiary integrity.
Education and Research
Historical Archives: Enhancing historical photographs and documents for educational use and research purposes.
Scientific Documentation: Improving the quality of scientific imagery for publication and presentation.
Digital Libraries: Upgrading digitized materials for better accessibility and preservation.
Academic Publishing: Enhancing images for scholarly publications where visual quality impacts credibility and readability.
Entertainment and Media
Film and Television: Enhancing low-quality source material for modern broadcast and streaming standards.
Gaming Industry: Upgrading texture assets and promotional materials for modern gaming platforms.
Music and Entertainment: Improving promotional imagery and historical documentation for artists and performers.
Publishing: Enhancing images for books, magazines, and digital publications.
Technical Implementation Strategies
Quality Assessment and Measurement
Objective Metrics: Using technical measurements like PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS to evaluate enhancement quality objectively.
Perceptual Evaluation: Human-centered assessment methods that consider how enhancements appear to actual viewers.
Comparative Analysis: Before-and-after evaluation techniques that highlight improvement areas and potential issues.
Context-Specific Evaluation: Tailoring quality assessment to specific use cases and viewing conditions.
Workflow Optimization
Batch Processing: Efficiently handling large collections of low-quality images with consistent enhancement standards.
Quality Control: Implementing systematic review processes to ensure enhancement quality meets professional standards.
File Management: Organizing enhanced images and maintaining version control for professional workflows.
Integration Strategies: Incorporating AI enhancement into existing photography and content creation workflows.
Hardware and Performance Considerations
Processing Requirements: Understanding computational needs for different enhancement tasks and image sizes.
Memory Management: Optimizing system resources for large image processing and batch operations.
Cloud vs. Local Processing: Choosing between local and cloud-based processing based on privacy, speed, and resource requirements.
Scalability Planning: Designing workflows that can handle increasing volumes of enhancement requests.
Advanced Techniques and Customization
Multi-Modal Enhancement
Text and Graphics: Specialized enhancement for images containing text, logos, and graphic elements.
Mixed Content: Handling images that combine photographic and graphic elements with different enhancement needs.
Artistic Content: Enhancing artwork, illustrations, and creative content while preserving artistic intent.
Technical Imagery: Specialized enhancement for scientific, medical, and technical imagery with specific quality requirements.
Creative Enhancement Options
Style Enhancement: Improving image quality while enhancing or maintaining specific artistic styles.
Era-Specific Processing: Applying enhancement techniques appropriate for different historical periods and photographic styles.
Genre Optimization: Tailoring enhancement for specific genres like portraits, landscapes, or architectural photography.
Mood Preservation: Maintaining the emotional tone and atmosphere of images while improving technical quality.
Specialized Applications
Microscopy Enhancement: Improving scientific imagery with specialized requirements for accuracy and detail.
Satellite and Aerial Imagery: Enhancing remote sensing data for better analysis and presentation.
Astronomical Photography: Specialized enhancement for space imagery with unique noise and quality characteristics.
Industrial Documentation: Enhancing technical and industrial photography for documentation and analysis purposes.
Quality Control and Best Practices
Enhancement Validation
Reference Comparison: Using high-quality reference images to validate enhancement accuracy and naturalness.
Multiple Algorithm Testing: Comparing results from different enhancement approaches to choose optimal methods.
Stakeholder Review: Implementing review processes with relevant stakeholders to ensure enhancement meets requirements.
Iterative Improvement: Using feedback to refine enhancement approaches and improve results over time.
Ethical Considerations
Authenticity Maintenance: Ensuring enhancement improves quality without creating misleading or false information.
Historical Accuracy: Preserving historical accuracy when enhancing archival and documentary imagery.
Cultural Sensitivity: Respecting cultural contexts and avoiding enhancement that might alter cultural or historical significance.
Transparency: Being clear about enhancement processes and their impact on original imagery.
Future Developments in Quality Enhancement
Emerging Technologies
Neural Architecture Search: Automated development of new AI architectures optimized for specific enhancement tasks.
Few-Shot Learning: AI systems that can adapt to new types of quality issues with minimal training data.
Real-Time Enhancement: Hardware and software developments enabling instant quality enhancement during capture or viewing.
Mobile Integration: Bringing professional-quality enhancement capabilities to smartphones and mobile devices.
Integration Opportunities
Camera Integration: Built-in AI enhancement in next-generation cameras and imaging devices.
Cloud Services: Advanced cloud-based enhancement services with unlimited processing power and storage.
API Development: Programming interfaces that allow integration of AI enhancement into custom applications and workflows.
Industry Standards: Development of industry standards for AI enhancement quality and compatibility.
Research Frontiers
Quantum Computing: Potential applications of quantum computing to image enhancement algorithms.
Neuromorphic Processing: Hardware designed to mimic brain processing for more efficient AI enhancement.
Multimodal AI: Systems that combine visual enhancement with understanding of context, text, and other information.
Sustainable AI: Developing more energy-efficient enhancement algorithms for environmental sustainability.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Enhancement Artifacts
Over-Processing: Identifying and avoiding enhancement that creates unnatural or artificial-looking results.
Inconsistent Results: Addressing variations in enhancement quality across different parts of an image.
Color Shifts: Managing color changes that may occur during enhancement processing.
Detail Loss: Preventing important detail from being lost during noise reduction or smoothing operations.
Performance Optimization
Processing Speed: Balancing enhancement quality with processing time for practical workflows.
Resource Management: Optimizing system resources for efficient enhancement of large images or batches.
Quality vs. Speed: Finding optimal settings for different use cases and time constraints.
Compatibility Issues: Ensuring enhanced images work properly across different systems and applications.
Conclusion
AI-powered low-quality photo enhancement represents one of the most practical and immediately beneficial applications of artificial intelligence in digital imaging. The ability to transform pixelated, compressed, and degraded images into high-definition, professional-quality photos opens up new possibilities for photographers, content creators, businesses, and anyone who works with digital images.
The technology has evolved from simple interpolation methods to sophisticated AI systems that can understand image content, identify specific quality issues, and apply targeted enhancements that preserve natural appearance while dramatically improving visual quality. Whether you're dealing with compressed social media images, low-resolution historical photographs, or any image suffering from quality limitations, modern AI enhancement provides accessible, powerful solutions.
RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer brings these advanced capabilities to users at every level, from casual photographers to professional imaging specialists. The key to success lies in understanding the types of quality issues your images face and applying appropriate enhancement techniques that improve quality while maintaining authenticity and natural appearance.
As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect even more impressive capabilities in quality enhancement. However, the fundamental principles of understanding image quality, choosing appropriate enhancement approaches, and balancing improvement with naturalness will remain essential skills for anyone working with digital imagery.
Don't let poor image quality limit your creative potential or professional capabilities. Explore the possibilities of AI quality enhancement and discover how these revolutionary tools can transform your most challenging images into stunning, high-definition masterpieces.
Ready to transform your low-quality images? Try RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer today and experience the remarkable difference AI can make in image quality improvement.
In the digital age, we're constantly dealing with images of varying quality. From heavily compressed social media uploads to low-resolution screenshots, poor-quality images are everywhere. However, 2025's advanced AI technology has revolutionized our ability to transform these seemingly unusable images into stunning, high-definition masterpieces.
This comprehensive guide explores the cutting-edge world of AI-powered low-quality photo enhancement, revealing how modern algorithms can breathe new life into pixelated, compressed, and degraded images. Whether you're dealing with family photos damaged by compression, low-resolution graphics that need upgrading, or any image suffering from quality issues, AI enhancement offers unprecedented solutions.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Low-Quality Image Problems
2. The Science of AI Quality Enhancement
3. Types of Quality Degradation AI Can Fix
4. Advanced Enhancement Algorithms
5. Professional Workflow Applications
6. Industry-Specific Use Cases
7. Technical Implementation Strategies
8. Future Developments in Quality Enhancement
Understanding Low-Quality Image Problems
The Nature of Digital Image Degradation
Digital images can suffer from quality loss through various mechanisms, each requiring different enhancement approaches. Understanding these degradation types is crucial for effective enhancement.
Compression Artifacts: When images are compressed for storage or transmission, data is lost, creating visible artifacts like blockiness, ringing, and color banding. JPEG compression, while efficient, introduces specific patterns of degradation that affect image quality.
Resolution Limitations: Low-resolution images lack the pixel density needed for sharp, detailed reproduction. This limitation becomes particularly problematic when images need to be displayed at larger sizes or higher resolutions.
Bit Depth Reduction: Color quantization reduces the number of available colors, creating posterization effects and loss of smooth gradations.
Sampling Issues: Poor sampling during image capture or conversion can introduce aliasing, moiré patterns, and other artifacts that degrade visual quality.
Sources of Image Quality Loss
Digital Camera Limitations: Early digital cameras, smartphone cameras, and budget imaging devices often produce images with inherent quality limitations due to sensor size, processing power, and lens quality constraints.
File Format Constraints: Aggressive compression settings in formats like JPEG can severely impact image quality, especially after multiple save operations.
Display and Capture Limitations: Screenshots from low-resolution displays, scanned images from poor-quality scanners, and images captured from video sources often suffer from quality issues.
Network Transmission: Images shared through social media platforms, messaging apps, and email systems are often automatically compressed, reducing quality significantly.
Historical Technology: Images created or processed with older technology may have quality limitations that modern enhancement can address.
The Science of AI Quality Enhancement
Deep Learning Approaches to Quality Improvement
Modern AI quality enhancement relies on sophisticated neural networks trained on massive datasets of high and low-quality image pairs. These systems learn to understand the relationship between degraded and pristine images, enabling them to make intelligent enhancement decisions.
Super-Resolution Networks: These specialized AI models can generate high-resolution details from low-resolution inputs by learning patterns and textures from training data. Unlike simple interpolation, these networks can create realistic detail that wasn't present in the original image.
Artifact Removal Networks: Dedicated AI systems trained specifically to identify and remove compression artifacts, noise, and other quality issues while preserving important image content.
Multi-Scale Processing: Advanced algorithms process images at multiple resolution levels simultaneously, ensuring consistent enhancement across different scales of detail.
Perceptual Loss Functions: Modern training approaches use perceptual similarity measures rather than simple pixel-wise comparisons, resulting in enhancements that look more natural to human viewers.
Computational Techniques
Residual Learning: Advanced network architectures that learn to predict the difference between low and high-quality images, enabling more effective training and better results.
Attention Mechanisms: AI systems that can focus on the most important areas of an image, applying stronger enhancement where it's needed most.
Progressive Enhancement: Multi-stage approaches that gradually improve image quality through successive refinement steps.
Domain Adaptation: Techniques that allow AI models trained on one type of image to work effectively on different types of content.
Types of Quality Degradation AI Can Fix
Compression-Related Issues
JPEG Blockiness: The characteristic 8x8 pixel blocks created by JPEG compression can be smoothed and eliminated while preserving important edge information.
Ringing Artifacts: Overshoot and undershoot artifacts around edges caused by compression can be identified and corrected.
Color Banding: Smooth color gradients broken into visible bands due to quantization can be restored to natural smoothness.
Mosquito Noise: High-frequency noise around edges and in textured areas can be reduced while maintaining detail clarity.
Resolution and Detail Issues
Pixelation: Blocky, pixelated images can be transformed into smooth, naturally detailed versions through intelligent interpolation and detail generation.
Jagged Edges: Aliasing and stair-stepping effects on diagonal lines and curves can be smoothed for more natural appearance.
Loss of Fine Detail: AI can reconstruct fine textures and details that were lost due to low resolution or poor capture quality.
Scale-Related Problems: Issues that arise when small images are displayed at larger sizes can be addressed through intelligent upscaling.
Color and Tonal Problems
Color Quantization: Reduced color palettes can be expanded to full color depth with natural-looking gradations.
Contrast Loss: Flat, low-contrast images can be enhanced to reveal hidden detail and improve visual impact.
Saturation Issues: Over-saturated or under-saturated colors can be corrected to more natural levels.
Gamma Problems: Incorrect gamma encoding can be detected and corrected for proper tonal reproduction.
Noise and Grain Issues
Digital Noise: Random pixel variations from sensor limitations or processing can be reduced while preserving image detail.
Compression Noise: Noise introduced by aggressive compression algorithms can be distinguished from image content and removed.
Scan Artifacts: Dust, scratches, and other artifacts from scanning processes can be identified and eliminated.
Film Grain: Excessive grain from high-ISO photography or film scanning can be reduced to appropriate levels.
Advanced AI Enhancement Algorithms
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs represent one of the most powerful approaches to image quality enhancement. These systems consist of two competing neural networks: a generator that creates enhanced images and a discriminator that evaluates their quality.
Enhanced SRGAN: Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks specifically designed for image upscaling and quality improvement.
Real-ESRGAN: Advanced versions trained on real-world degraded images rather than artificially degraded ones, providing better performance on actual low-quality photos.
Progressive Growing: GAN architectures that generate increasingly higher resolution images through successive stages.
Style Transfer GANs: Systems that can improve image quality while maintaining or enhancing artistic style.
Transformer-Based Approaches
Vision Transformers: Attention-based models that can understand global image context for more coherent enhancement decisions.
Swin Transformers: Hierarchical transformers that efficiently process images at multiple scales for comprehensive quality improvement.
Cross-Attention Mechanisms: Systems that can correlate information across different parts of an image for better enhancement consistency.
Hybrid Approaches
CNN-Transformer Hybrids: Combinations that leverage the local feature extraction of CNNs with the global understanding of transformers.
Multi-Task Learning: Systems trained simultaneously on multiple quality enhancement tasks for more robust performance.
Ensemble Methods: Combining multiple specialized models for optimal results across different types of degradation.
Professional Workflow Applications
Photography and Imaging Professionals
Print Preparation: Enhancing low-resolution images for large-format printing, enabling the use of images that would otherwise be unsuitable for print reproduction.
Archive Digitization: Improving the quality of digitized historical photographs, documents, and artwork for preservation and display purposes.
Client Deliverables: Enhancing images for professional delivery when original capture wasn't optimal due to circumstances or equipment limitations.
Stock Photography: Upgrading older stock images to modern quality standards for continued commercial viability.
Content Creation and Media
Social Media Optimization: Enhancing images that have been degraded by social platform compression for better visual impact.
Video Production: Improving still frames extracted from video for use in promotional materials and documentation.
Website Development: Enhancing images for web use, ensuring they look sharp across different devices and screen resolutions.
Digital Marketing: Improving image quality for advertising and promotional materials where high visual impact is crucial.
E-commerce and Retail
Product Photography: Enhancing product images that may have been captured with limited equipment or in challenging conditions.
Catalog Management: Upgrading existing product images to maintain consistent quality standards across large inventories.
Marketplace Optimization: Improving image quality for better performance on e-commerce platforms where visual quality affects sales.
Brand Consistency: Ensuring all brand imagery meets modern quality standards regardless of original capture conditions.
Using RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer
Comprehensive Enhancement Process
RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer tool provides state-of-the-art quality improvement through an intuitive, professional-grade interface:
Step 1: Image Analysis and Assessment
Upload your low-quality image and let the AI automatically analyze the types of degradation present, identifying specific issues like compression artifacts, pixelation, or noise.
Step 2: Intelligent Enhancement Selection
The AI determines the optimal enhancement strategies based on the specific quality issues detected, selecting appropriate algorithms for maximum improvement.
Step 3: Multi-Stage Processing
Images undergo sophisticated multi-stage enhancement, with different algorithms addressing specific quality issues in optimal sequence.
Step 4: Quality Optimization
The system fine-tunes enhancement parameters to achieve the best possible balance between quality improvement and natural appearance.
Step 5: Output Generation
Generate enhanced images in multiple resolutions and formats suitable for your specific use case.
Enhancement Customization Options
Artifact Reduction Strength: Control the aggressiveness of compression artifact removal to balance smoothness with detail preservation.
Detail Enhancement Level: Adjust how much fine detail the AI generates, allowing for subtle or dramatic improvements.
Color Restoration: Fine-tune color enhancement to achieve natural color reproduction or creative color grading.
Noise Reduction: Balance noise removal with detail preservation for optimal results in different viewing contexts.
Resolution Scaling: Choose output resolution based on intended use, from web display to large-format printing.
Industry-Specific Applications
Healthcare and Medical Imaging
Historical Medical Records: Enhancing old medical photographs and documentation for modern digital archives.
Telemedicine Support: Improving image quality for remote medical consultations where image clarity is crucial for diagnosis.
Educational Materials: Upgrading medical education imagery for modern display and learning systems.
Research Documentation: Enhancing historical medical research imagery for contemporary analysis and publication.
Legal and Forensic Applications
Evidence Enhancement: Improving the quality of photographic evidence while maintaining authenticity and legal admissibility.
Historical Document Processing: Enhancing scanned legal documents and photographs for better readability and preservation.
Surveillance Image Improvement: Upgrading security camera footage and images for better identification and analysis.
Court Presentation: Preparing enhanced images for clear courtroom display while maintaining evidentiary integrity.
Education and Research
Historical Archives: Enhancing historical photographs and documents for educational use and research purposes.
Scientific Documentation: Improving the quality of scientific imagery for publication and presentation.
Digital Libraries: Upgrading digitized materials for better accessibility and preservation.
Academic Publishing: Enhancing images for scholarly publications where visual quality impacts credibility and readability.
Entertainment and Media
Film and Television: Enhancing low-quality source material for modern broadcast and streaming standards.
Gaming Industry: Upgrading texture assets and promotional materials for modern gaming platforms.
Music and Entertainment: Improving promotional imagery and historical documentation for artists and performers.
Publishing: Enhancing images for books, magazines, and digital publications.
Technical Implementation Strategies
Quality Assessment and Measurement
Objective Metrics: Using technical measurements like PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS to evaluate enhancement quality objectively.
Perceptual Evaluation: Human-centered assessment methods that consider how enhancements appear to actual viewers.
Comparative Analysis: Before-and-after evaluation techniques that highlight improvement areas and potential issues.
Context-Specific Evaluation: Tailoring quality assessment to specific use cases and viewing conditions.
Workflow Optimization
Batch Processing: Efficiently handling large collections of low-quality images with consistent enhancement standards.
Quality Control: Implementing systematic review processes to ensure enhancement quality meets professional standards.
File Management: Organizing enhanced images and maintaining version control for professional workflows.
Integration Strategies: Incorporating AI enhancement into existing photography and content creation workflows.
Hardware and Performance Considerations
Processing Requirements: Understanding computational needs for different enhancement tasks and image sizes.
Memory Management: Optimizing system resources for large image processing and batch operations.
Cloud vs. Local Processing: Choosing between local and cloud-based processing based on privacy, speed, and resource requirements.
Scalability Planning: Designing workflows that can handle increasing volumes of enhancement requests.
Advanced Techniques and Customization
Multi-Modal Enhancement
Text and Graphics: Specialized enhancement for images containing text, logos, and graphic elements.
Mixed Content: Handling images that combine photographic and graphic elements with different enhancement needs.
Artistic Content: Enhancing artwork, illustrations, and creative content while preserving artistic intent.
Technical Imagery: Specialized enhancement for scientific, medical, and technical imagery with specific quality requirements.
Creative Enhancement Options
Style Enhancement: Improving image quality while enhancing or maintaining specific artistic styles.
Era-Specific Processing: Applying enhancement techniques appropriate for different historical periods and photographic styles.
Genre Optimization: Tailoring enhancement for specific genres like portraits, landscapes, or architectural photography.
Mood Preservation: Maintaining the emotional tone and atmosphere of images while improving technical quality.
Specialized Applications
Microscopy Enhancement: Improving scientific imagery with specialized requirements for accuracy and detail.
Satellite and Aerial Imagery: Enhancing remote sensing data for better analysis and presentation.
Astronomical Photography: Specialized enhancement for space imagery with unique noise and quality characteristics.
Industrial Documentation: Enhancing technical and industrial photography for documentation and analysis purposes.
Quality Control and Best Practices
Enhancement Validation
Reference Comparison: Using high-quality reference images to validate enhancement accuracy and naturalness.
Multiple Algorithm Testing: Comparing results from different enhancement approaches to choose optimal methods.
Stakeholder Review: Implementing review processes with relevant stakeholders to ensure enhancement meets requirements.
Iterative Improvement: Using feedback to refine enhancement approaches and improve results over time.
Ethical Considerations
Authenticity Maintenance: Ensuring enhancement improves quality without creating misleading or false information.
Historical Accuracy: Preserving historical accuracy when enhancing archival and documentary imagery.
Cultural Sensitivity: Respecting cultural contexts and avoiding enhancement that might alter cultural or historical significance.
Transparency: Being clear about enhancement processes and their impact on original imagery.
Future Developments in Quality Enhancement
Emerging Technologies
Neural Architecture Search: Automated development of new AI architectures optimized for specific enhancement tasks.
Few-Shot Learning: AI systems that can adapt to new types of quality issues with minimal training data.
Real-Time Enhancement: Hardware and software developments enabling instant quality enhancement during capture or viewing.
Mobile Integration: Bringing professional-quality enhancement capabilities to smartphones and mobile devices.
Integration Opportunities
Camera Integration: Built-in AI enhancement in next-generation cameras and imaging devices.
Cloud Services: Advanced cloud-based enhancement services with unlimited processing power and storage.
API Development: Programming interfaces that allow integration of AI enhancement into custom applications and workflows.
Industry Standards: Development of industry standards for AI enhancement quality and compatibility.
Research Frontiers
Quantum Computing: Potential applications of quantum computing to image enhancement algorithms.
Neuromorphic Processing: Hardware designed to mimic brain processing for more efficient AI enhancement.
Multimodal AI: Systems that combine visual enhancement with understanding of context, text, and other information.
Sustainable AI: Developing more energy-efficient enhancement algorithms for environmental sustainability.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Enhancement Artifacts
Over-Processing: Identifying and avoiding enhancement that creates unnatural or artificial-looking results.
Inconsistent Results: Addressing variations in enhancement quality across different parts of an image.
Color Shifts: Managing color changes that may occur during enhancement processing.
Detail Loss: Preventing important detail from being lost during noise reduction or smoothing operations.
Performance Optimization
Processing Speed: Balancing enhancement quality with processing time for practical workflows.
Resource Management: Optimizing system resources for efficient enhancement of large images or batches.
Quality vs. Speed: Finding optimal settings for different use cases and time constraints.
Compatibility Issues: Ensuring enhanced images work properly across different systems and applications.
Conclusion
AI-powered low-quality photo enhancement represents one of the most practical and immediately beneficial applications of artificial intelligence in digital imaging. The ability to transform pixelated, compressed, and degraded images into high-definition, professional-quality photos opens up new possibilities for photographers, content creators, businesses, and anyone who works with digital images.
The technology has evolved from simple interpolation methods to sophisticated AI systems that can understand image content, identify specific quality issues, and apply targeted enhancements that preserve natural appearance while dramatically improving visual quality. Whether you're dealing with compressed social media images, low-resolution historical photographs, or any image suffering from quality limitations, modern AI enhancement provides accessible, powerful solutions.
RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer brings these advanced capabilities to users at every level, from casual photographers to professional imaging specialists. The key to success lies in understanding the types of quality issues your images face and applying appropriate enhancement techniques that improve quality while maintaining authenticity and natural appearance.
As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect even more impressive capabilities in quality enhancement. However, the fundamental principles of understanding image quality, choosing appropriate enhancement approaches, and balancing improvement with naturalness will remain essential skills for anyone working with digital imagery.
Don't let poor image quality limit your creative potential or professional capabilities. Explore the possibilities of AI quality enhancement and discover how these revolutionary tools can transform your most challenging images into stunning, high-definition masterpieces.
Ready to transform your low-quality images? Try RestoreAI's Low Quality Enhancer today and experience the remarkable difference AI can make in image quality improvement.